얕은 복사 (Swallow Copy)
원본 객체의 non-static 필드를 복사하여 새로운 객체로 생성하는 것.
새로운 객체를 생성할 때 원본 객체의 필드 타입으로 나뉜다.
1. 원본 객체가 non-primitive 타입의 필드를 가지고 있을 때.
2. 원본 객체가 primitive 타입의 필드를 가지고 있을 때.
*primitive 타입 : int, float, double, char, byte, short, long, boolean*
1. 원본 객체가 non-primitives 타입의 필드(변수)를 가질 경우,
원본 객체의 non-primitive 타입의 필드들을 복사하여 새로운 객체를 생성한다.
그 결과, 원본 객체와 얕은 복사의 결과인 새로운 객체는 동일한 non-primitive 타입 필드들을 가진다.
즉, 원본 객체 or 얕은 복사 결과 객체의 non-primitive 필드 중 변화가 생기면 그 값을 공유한다.
[예시]
#1. Person 클래스를 만들고, Person의 친구들을 나타내는 List<String> 필드를 생성하자.
class Person implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private final List<String> friends;
public Person(String name, List<String> friends) {
this.name = name;
this.friends = friends;
}
public List<String> getFriends() {
return friends;
}
@Override
protected Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Person)super.clone();
}
}
#2. Person 객체를 생성하고, clone 메서드를 사용해서 얕은 복사 객체를 생성해보자.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
List<String> friendsList = new ArrayList<>();
friendsList.add("Alice");
friendsList.add("Bob");
Person p1 = new Person("John", friendsList);
Person p2 = p1.clone();
}
}p1 = 원본 Person 객체.
p2 = p1의 얕은 복사로 생성한 객체. (원본 객체의 non-static 필드를 복사하여 새로운 객체로 생성)
즉 p1과 p2는 서로 다른 객체이다.
하지만 두 객체에 공통적으로 있는 List<String> friends 필드는 동일한 ArrayList 개체를 참조한다.
만약 두 객체 중 한 객체의 friends 필드에 변화가 생긴다면 다른 객체에도 변화가 적용된다.
[예시] 얕은 복사로 생성한 p1의 복사 객체인 p2의 friends 필드에 "David" 를 추가
p2.getFriends().add("David");p1 객체의 friends 필드를 조회하면 p2와 동일하게 p1의 friends 필드에도 David이 포함된 걸 알 수 있다.
System.out.println("p1.getFriends() = " + p1.getFriends());
2. 원본 객체가 primitive 타입의 필드(변수)를 가질 경우,
얕은 복사로 생성되는 새로운 객체는 원본 객체의 primitive 타입의 필드를 그대로 복사하여 생성된다.
하지만 원본 객체와 얕은 복사로 생성된 객체는 각 primitive 타입의 필드를 가지지만,
두 객체들은 primitive 타입의 필드들의 값을 공유하지 않는 독립적인 객체가 된다.
[예시]
class Person implements Cloneable {
private String name;
int age;
private final List<String> friends;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.friends = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addFriend(String friend) {
friends.add(friend);
}
public List<String> getFriends() {
return friends;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
protected Person clone() {
try {
return (Person) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to clone Person Object", e);
}
}
}위의 예제에서 Person 클래스에 int age는 primitive 타입의 필드이고, friends는 non-primitive 타입 필드.
[예시]
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("Alice",30);
p1.addFriend("Bob");
Person p2 = p1.clone();
p2.addFriend("Charlie");
System.out.println("P1 friends: = " + p1.getFriends());
System.out.println("P2 friends: = " + p2.getFriends());
p2.age = 35;
System.out.println("P1 age: = " + p1.getAge());
System.out.println("P2 age: = " + p2.getAge());
}
}1. Person 클래스의 객체 p1 을 생성.
2. p1의 non-primitive 필드인 friends에 "Bob"을 추가함.
3. p2의 non-primitive 필드인 friends에 "Charlie" 추가함.
3. p1을 대상으로 얕은 복사를 통해 p2 를 생성.
4. p2의 primitive 필드인 age를 별도로 설정.
4. p1, p2의 friends 필드와 age 필드를 출력.
[결과]
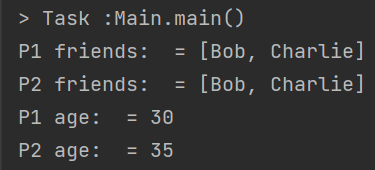
non-primitive 필드의 값은 p1, p2가 서로 공유하는 반면,
primitive 필드의 값은 p1, p2가 공유하지 않고 독립적인 값을 갖는다.
[정리]
#얕은 복사
1. 원본 객체의 non-static 필드를 복사하여 새로운 객체에 할당.
2. 원본 객체가 non-primitive 필드를 가지고 있으면, non-primitive 필드를 복사하고 원본 객체와 공유 O.
3. 원본 객체가 primitive 필드를 가지고 있으면, 그 primitive 필드들을 복사하지만 원본 객체와 공유 X.
깊은 복사 (Deep Copy)
원본 객체의 모든 필드 (static or non-static / primitive or non-primitive 상관없이)를 복사하여
원본 객체와 완전히 독립된 새로운 객체를 생성하고 할당한다.
[예제]
public class Person{
private String name;
private List<String> friends;
public Person(String name, List<String> friends) {
this.name = name;
this.friends = friends;
}
public Person deepCopy() {
String newName = this.name;
List<String> newFriends = new ArrayList<>();
for(String friend : this.friends) {
newFriends.add(friend);
}
return new Person(newName, newFriends);
}
public void addFriend(String friend){
friends.add(friend);
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public List<String> getFriends() {
return friends;
}
}Person 클래스 타입의 deepCopy() 메서드 생성.
이 메서드는 원본 객체의 primitive, non-primitive 필드들을 복사하여 새로운 Person 객체를 생성한다.
[deepCopy() 메서드 설명]
1. Person 클래스의 non-primitive 필드 String name 복사.
String newName = this.name
> 우항의 this.name은 Person 클래스의 non-primitive 필드 String name 을 나타낸다.
String 은 불변 객체 타입이므로 새로운 String 객체를 생성해 기존의 String 객체 값을 할당할 수 있다.
2. Person 클래스의 non-primitive 필드 List<String> friends 복사.
A. 새로운 List<String> newFriends = new ArrayList<>(); 생성.
B. for(String friend : this.friends) {
newFriends.add(friend);
}
for()문 우항의 this.friends 는 Person 클래스의 non-primitive 필드 List<String> friends 를 나타낸다.
즉 우항의 friends 로 부터 하나씩 꺼내서 String friend 객체에 담는다.
C. 새로 생성한 newFriends List 객체에 friend 객체를 추가한다.
3. Person 클래스의 non-primitive 필드 2개 String name, List<String> friends를 복사한
String newName, List<String> newFriends 를 사용한 새로운 Person 객체를 반환. => 깊은 복사
[예제]
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 깊은 복사 예제
List<String> friendsList = new ArrayList<>();
friendsList.add("Bob");
Person p1 = new Person("Alice", friendsList);
Person p2 = p1.deepCopy();
p2.addFriend("Charlie");
System.out.println("p1 friends: = " + p1.getFriends());
System.out.println("p2 friends: = " + p2.getFriends());
}
}1. Person 클래스의 non-primitive 필드 List<String> 객체 생성하고 "Bob" 추가.
2. Person 객체 p1 생성.
3. Person p1 객체의 깊은 복사로 p2 객체 생성.
4. p2 객체의 List<String>객체에 "Charlie" 추가
5. p1, p2의 List<String> 객체 출력.
[결과]
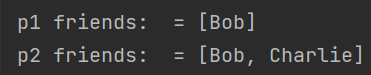
즉, 원본 객체 p1과 p1의 깊은 복사 객체 p2는 필드의 값을 공유하지 않는다.
[정리]
#얕은 복사
1. 원본 객체의 non-static 필드를 복사하여 새로운 객체에 할당.
2. 원본 객체가 non-primitive 필드를 가지고 있으면, non-primitive 필드를 복사하고 원본 객체와 공유 O.
3. 원본 객체가 primitive 필드를 가지고 있으면, 그 primitive 필드들을 복사하지만 원본 객체와 공유 X.
#깊은 복사
1. 원본 객체의 모든 필드 (non-static/static, primitive/non-primitive 상관없이)를 복사하여
새로운 객체를 생성하고 할당함.
2. 새롭게 생성된 깊은 복사의 객체와 원본 객체는 같은 필드들을 가지고 있지만 필드 값을 공유하지 않음
'백엔드 기술 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자료구조 - Stack, Queue 차이점 (0) | 2023.05.15 |
|---|---|
| Synchronized 키워드의 이해 (0) | 2023.04.29 |
| Optional<T> 클래스란 ? (0) | 2023.04.21 |
| Multi-Thread & Multi Process (0) | 2023.04.20 |
| SingleTon 디자인 패턴 (0) | 2023.04.20 |



